Urinary system in cats
Anatomy of the Feline Urinary System: Understanding the Structure and Function
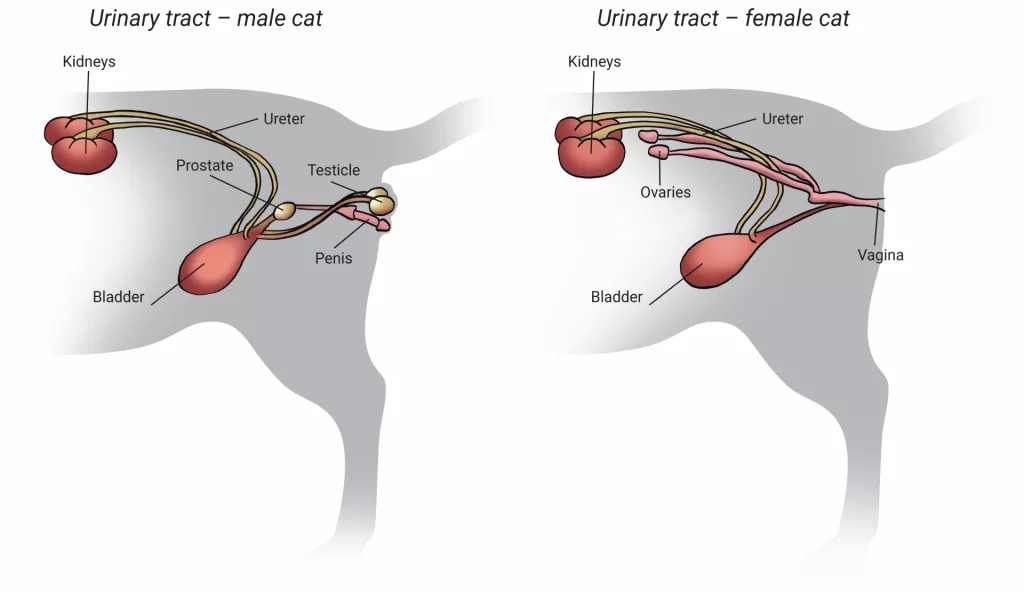
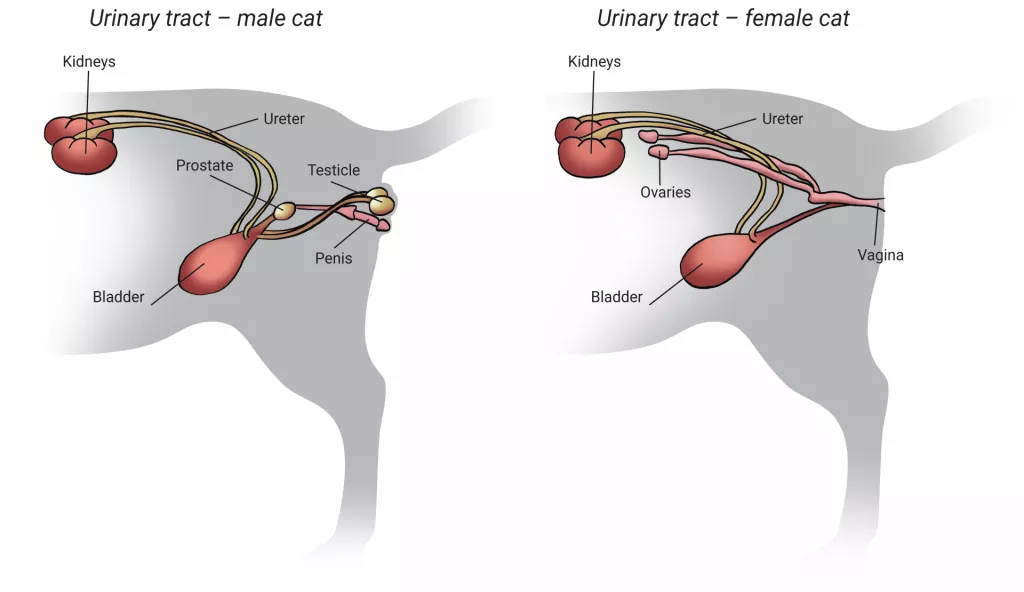
The feline urinary system plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of our feline friends. Understanding its structure and function can help us comprehend the complexities of this essential system. The urinary system consists of various components, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra.
At the core of the feline urinary system lie the kidneys, which serve as the primary filtration system. These bean-shaped organs are responsible for removing waste products, chemicals, and excess water from the blood, producing urine in the process. The urine then travels through the ureters, which are narrow tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder, a muscular sac situated in the abdominal cavity, acts as a temporary reservoir for urine until it is voluntarily eliminated through the urethra.
Common Urinary Disorders in Cats: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Urinary disorders are a common issue in cats and can be caused by various factors. One of the primary causes is urinary tract infections, which occur when bacteria enter the urinary system and multiply. Additionally, bladder stones, which are mineral deposits that form in the bladder, can also lead to urinary disorders. These stones can cause irritation, blockages, and discomfort for cats. Other possible causes include urinary blockages, tumors, and certain medications.
Recognizing the symptoms of urinary disorders in cats is crucial for timely intervention. Some common signs to look out for include frequent urination, difficulty or pain while urinating, blood in the urine, and urinating outside the litter box. Cats may also experience excessive grooming of the genital area, loss of appetite, lethargy, and even vomiting. If your cat displays any of these symptoms, it is important to seek veterinary attention promptly.
Treatment for urinary disorders in cats depends on the underlying cause. In the case of urinary tract infections, antibiotics are commonly prescribed to eliminate the bacteria. Bladder stones may require surgical removal or, in some cases, a special diet designed to dissolve the stones. Urinary blockages often necessitate emergency intervention to relieve the obstruction. Additionally, managing stress and maintaining a healthy diet can help prevent and manage urinary disorders in cats. Consulting with your veterinarian is essential to determine the most appropriate course of treatment for your furry friend.
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD): Exploring the Different Types
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) is a common condition that affects cats of all ages and breeds. It is characterized by a variety of urinary symptoms and can be caused by several different factors. Understanding the different types of FLUTD is crucial in order to provide the appropriate treatment and management for affected cats.
The first type of FLUTD is called Feline Idiopathic Cystitis, which refers to inflammation of the bladder without a clear underlying cause. This type is often seen in younger cats and is believed to be related to stress and changes in the environment. Symptoms can include frequent urination, straining to urinate, blood in the urine, and urinating outside the litter box.
Another type of FLUTD is Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs), which occur when bacteria enter the urinary system and cause an infection. Cats with UTIs may exhibit similar symptoms as Feline Idiopathic Cystitis, but may also show signs of discomfort and pain while urinating. UTIs are more common in older cats, particularly those with other medical conditions such as kidney disease or diabetes.
Lastly, FLUTD can also be caused by the formation of urinary stones or crystals in the bladder or urethra, a condition known as Feline Urolithiasis. These stones can block the passage of urine, leading to urinary obstruction, which is a life-threatening emergency. Symptoms of urolithiasis include difficulty or inability to urinate, crying out in pain, and lethargy. This type of FLUTD often requires immediate veterinary intervention to relieve the obstruction and prevent further complications.
It is important to remember that these are just a few examples of the different types of FLUTD. Each case is unique, and the specific type of FLUTD can vary based on individual factors and underlying causes. Consulting with a veterinarian is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options for cats affected by FLUTD.
The Role of Diet in Maintaining a Healthy Urinary System for Cats
One of the key factors in maintaining a healthy urinary system in cats is the diet they consume. The type and quality of food can have a profound impact on their urinary health. Cats, being obligate carnivores, require a high-protein diet that is rich in animal-based ingredients. This is because protein plays a crucial role in maintaining the pH balance of the urine, preventing the formation of crystals and stones that can lead to urinary issues. It is important to choose a cat food that contains a sufficient amount of high-quality protein to support the overall health of the urinary system.
In addition to protein, the moisture content of the diet also plays a vital role in promoting urinary health in cats. Unlike humans, cats have a low thirst drive and rely on their food to meet their hydration needs. A dry diet can lead to concentrated and overly acidic urine, which increases the risk of urinary tract infections and the formation of urinary crystals. Providing wet or moist food options can help increase their water intake and ensure that they maintain proper hydration. It is also recommended to provide fresh water sources in multiple locations to encourage regular drinking.
Recognizing the Signs of Urinary Problems in Cats: What to Look Out For
Feline urinary problems can be challenging to recognize, as cats are known for hiding their discomfort. However, being aware of the signs can help you identify potential issues early on and seek appropriate veterinary care. One common indicator of urinary problems in cats is frequent urination. If you notice your feline friend using the litter box more often than usual or making repeated trips to urinate outside, it could be a sign of a urinary issue.
Another important sign to watch out for is straining during urination. If your cat appears to be straining, squatting for an extended period, or showing any signs of discomfort while urinating, it is essential to take note. Additionally, keep an eye out for any changes in the color, consistency, or odor of your cat’s urine. Blood in the urine, cloudy appearance, or a strong unpleasant smell can all indicate a potential problem with the urinary system. Paying attention to these signs can play a crucial role in early detection and successful treatment of urinary issues in cats.
Diagnostic Tests for Evaluating Feline Urinary Issues: From Urinalysis to Imaging
Urinalysis is one of the most common diagnostic tests used to evaluate feline urinary issues. This simple and non-invasive test involves analyzing a urine sample for various parameters such as pH, specific gravity, presence of blood cells, crystals, bacteria, and other substances. Urinalysis helps veterinarians gather valuable information about the cat’s urinary health, identify the presence of infections, assess the functioning of the kidneys, and detect any abnormalities in the urine composition. By examining the specific characteristics of the urine, veterinarians can gain insights into potential underlying causes of the urinary issues and determine an appropriate treatment plan.
In more complicated cases or when further information is needed, imaging techniques such as X-rays, ultrasound, or even specialized imaging like CT scans or MRIs may be employed. These imaging modalities provide detailed visualizations of the urinary system, allowing veterinarians to identify the presence of stones, tumors, or structural abnormalities within the kidneys, bladder, or urethra. Additionally, these tests can help assess the overall health and functioning of the urinary organs. By utilizing these diagnostic tools, veterinarians can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying causes of feline urinary issues, leading to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans for each individual cat.
Managing Feline Urinary Tract Infections: Antibiotics and Beyond
Feline urinary tract infections (UTIs) can be painful and debilitating for cats. While antibiotics are often the go-to treatment for these infections, it is important to explore other management strategies as well. Antibiotics are effective in eliminating the bacteria causing the infection, but they may also disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the urinary tract. This can lead to recurring UTIs or the development of antibiotic resistance.
One alternative approach to managing feline UTIs is through the use of natural remedies. Some pet owners prefer to try cranberry supplements or homeopathic remedies to help support their cat’s urinary health. However, it is important to note that there is limited scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of these alternative treatments. Consulting with a veterinarian is crucial to ensure the best course of action for your cat’s specific situation. In addition to exploring alternative treatments, maintaining a healthy diet and reducing stress levels can also play a significant role in preventing and managing UTIs in cats.
Cat Stress and Its Impact on the Urinary System: How to Minimize Risk
Stress can significantly impact a cat’s urinary system, leading to various urinary issues. Cats are highly sensitive animals, and changes in their environment, routine, or social interactions can trigger stress. This stress can manifest in different ways, such as excessive grooming, changes in appetite and water intake, urinating outside the litter box, or avoiding the litter box altogether. These changes can disrupt the cat’s urinary system and increase the risk of developing urinary tract infections or other urinary disorders.
To minimize the risk of stress-related urinary problems in cats, it is crucial to create a calm and stable environment for them. Providing a consistent routine with regular feeding times, playtime, and social interactions can help alleviate stress. Additionally, creating a safe and comfortable space where the cat can retreat and feel secure, such as a quiet corner or a designated hiding spot, can be beneficial. Introducing environmental enrichment, such as interactive toys or scratching posts, can also help to reduce stress and provide mental stimulation for the cat. Ultimately, by creating a stress-free environment and ensuring the cat’s overall well-being, the risk of urinary issues can be minimized.
What is the feline urinary system?
The feline urinary system refers to the organs and structures involved in the production, storage, and elimination of urine in cats. It includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
What are some common urinary disorders in cats?
Some common urinary disorders in cats include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, urinary blockages, and feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD).
How can stress impact the urinary system in cats?
Stress can have a significant impact on the urinary system in cats. It can lead to an increased risk of developing urinary disorders such as FLUTD, urinary blockages, and urinary tract infections.
What are the symptoms of urinary problems in cats?
The symptoms of urinary problems in cats may include frequent urination, blood in the urine, straining to urinate, urinating outside the litter box, and vocalizing while urinating.
How can I minimize the risk of cat stress on the urinary system?
To minimize the risk of cat stress on the urinary system, it is important to provide a calm and stable environment for your cat. This can be achieved through regular routine, sufficient play and exercise, and minimizing exposure to stressors such as loud noises or changes in the household.
What role does diet play in maintaining a healthy urinary system for cats?
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy urinary system for cats. A balanced and appropriate diet can help prevent the formation of urinary crystals or stones and promote overall urinary health.
What diagnostic tests are used to evaluate feline urinary issues?
Diagnostic tests commonly used to evaluate feline urinary issues include urinalysis, urine culture, blood tests, X-rays, and ultrasounds.
How are feline urinary tract infections managed?
Feline urinary tract infections are typically managed with antibiotics. However, depending on the severity and underlying cause, additional treatments such as pain management and dietary modifications may be necessary.
Can stress alone cause urinary problems in cats?
While stress can increase the risk of urinary problems in cats, it is usually not the sole cause. Other factors such as diet, genetics, and underlying medical conditions can also contribute to the development of urinary disorders.