Lymphatic system of felines
Lymph Nodes: Understanding the Feline Lymphatic System
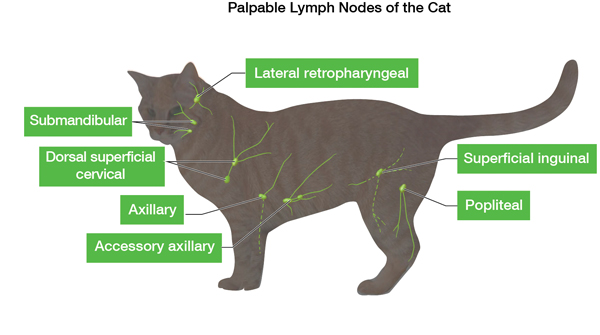
Lymph nodes play a crucial role in the feline lymphatic system, serving as important components of the immune response. These small, bean-shaped structures are found throughout a cat’s body and are interconnected by lymphatic vessels. Acting as filtration sites, they help to purify the lymph fluid by trapping and removing foreign particles such as bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances.
Within the lymph nodes, specialized immune cells called lymphocytes are found. These cells are responsible for recognizing and destroying pathogens, as well as coordinating immune responses. As lymph fluid flows through the lymph nodes, lymphocytes are activated and begin to multiply, aiding in the body’s defense against infections and diseases. Additionally, lymph nodes also serve as meeting points where immune cells interact, further enhancing immune responses and ensuring effective defense mechanisms within the feline body.
Lymphatic Vessels: The Transport Network of Feline Immunity

Feline immune system relies on a complex network of vessels known as the lymphatic vessels. These vessels play a crucial role in transporting lymph, a clear fluid that contains immune cells, throughout the cat’s body. Similar to the circulatory system, the lymphatic vessels form a vast network that reaches every corner of the feline anatomy, ensuring a comprehensive coverage of the immune response.
The lymphatic vessels act as a highway system for immune cells, allowing them to travel to different parts of the body and carry out their important tasks. These vessels are highly interconnected and can be found alongside blood vessels and nerves. They have thin walls which are permeable, allowing immune cells and other substances to enter and exit. The lymphatic vessels not only transport immune cells but also help in the removal of waste products and excess fluid from the tissues, maintaining a healthy balance within the feline immune system.
Primary Lymphoid Organs: Where Feline Lymphocytes are Born
The feline immune system is a remarkable network designed to protect the body from harmful invaders. At the core of this system are the primary lymphoid organs, where feline lymphocytes are born. These organs play a crucial role in the development and maturation of lymphocytes, which are key players in the immune response.
The primary lymphoid organs include the bone marrow and the thymus gland. The bone marrow is responsible for producing and maturing B lymphocytes, also known as B cells. These cells are essential in producing antibodies that help fight off infections. On the other hand, the thymus gland is responsible for the development and maturation of T lymphocytes, or T cells. T cells are crucial in regulating the immune response and directly attacking infected cells. Together, these primary lymphoid organs provide the foundation for a strong and effective immune system in felines.
Secondary Lymphoid Organs: The Meeting Points of Feline Immune Cells
The feline immune system is a complex network of cells and organs that work together to defend the body against infections and diseases. One crucial component of this system is the secondary lymphoid organs, which serve as the meeting points for feline immune cells. These organs include the lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, and Peyer’s patches.
The lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures found throughout the body, where immune cells called lymphocytes gather and interact with pathogens. When an infection enters the body, lymphocytes in nearby lymph nodes quickly multiply and attack the invading microorganisms. The spleen, on the other hand, filters the blood and acts as a reservoir of lymphocytes and other immune cells. Tonsils, located at the back of the throat, play a crucial role in preventing bacteria and viruses from entering the respiratory and digestive systems. Lastly, Peyer’s patches, found in the lining of the intestines, sample the contents of the gut for potential threats and activate immune responses when necessary. The intricate coordination of these secondary lymphoid organs ensures that feline immune cells are efficiently deployed to sites of infection, promoting a strong and effective immune response.
Lymphatic Drainage: Exploring the Flow of Feline Lymph
Feline lymphatic drainage is a crucial process that ensures the smooth flow of lymphatic fluid throughout the body. Lymph, a clear fluid that contains white blood cells, proteins, and waste products, is transported via a complex network of lymphatic vessels. Similar to a drainage system, the lymphatic vessels serve to collect the lymphatic fluid from the tissues and organs and direct it towards the lymph nodes for filtration.
The lymphatic vessels in cats are distributed throughout the body, intricately intertwined with blood vessels. They have one-way valves that prevent backflow and help maintain a unidirectional flow of lymph towards the thoracic duct, the largest lymphatic vessel in the feline body. From there, the lymphatic fluid enters the bloodstream, allowing the immune cells and other components of the lymphatic system to circulate throughout the body and carry out their protective functions.
Overall, the process of feline lymphatic drainage is essential for maintaining a proper balance within the body’s immune system. It ensures the removal of toxins, waste products, and pathogens from the tissues, while also facilitating the transportation of immune cells to areas where they are needed the most. Understanding the flow of feline lymph provides valuable insight into the functioning of the lymphatic system and its role in maintaining optimal health for our feline companions.
Lymphatic Filtration: How Feline Lymph Nodes Purify the System
Feline lymph nodes play a crucial role in purifying the lymphatic system. These small, bean-shaped structures are strategically located throughout the body, acting as filters that trap and remove harmful substances and foreign particles from the lymph fluid. As lymph fluid flows through a network of vessels, it eventually reaches the lymph nodes, where the purification process begins.
Within the lymph nodes, there are specialized immune cells called lymphocytes, which actively scan the lymphatic fluid for any potential threats. When lymphocytes encounter harmful substances, such as bacteria, viruses, or damaged cells, they initiate an immune response. This response can involve the activation of other immune cells, the production of antibodies, and the destruction of foreign invaders. By performing these vital functions, feline lymph nodes help maintain a healthy immune system and ensure the well-being of the cat.
Lymphatic System and Disease: The Impact of Infections on Felines
Infections can have a significant impact on the lymphatic system of felines. When a cat is exposed to an infectious agent, such as a bacteria or virus, it can trigger an immune response that involves the lymphatic system. The lymph nodes, which are small bean-shaped organs located throughout the body, play a crucial role in this response. They act as filters, trapping and destroying pathogens that enter the lymphatic fluid. When an infection occurs, the lymph nodes can become swollen and tender as they work to eliminate the harmful invaders. This response is a sign that the lymphatic system is actively engaged in fighting off the infection and protecting the feline’s overall health.
Infections can also affect the lymphatic vessels, which are the transport network of the feline immune system. These vessels carry the lymphatic fluid, containing immune cells, throughout the body. When an infection occurs, the lymphatic vessels can become inflamed and may even develop blockages. This can disrupt the normal flow of the lymphatic fluid, hindering the immune response and potentially allowing the infection to spread. Furthermore, infections can also lead to the enlargement of lymphoid tissues, such as the tonsils and adenoids, which are secondary lymphoid organs. These changes in the lymphatic system can impact a feline’s ability to fend off infections and may require veterinary intervention to restore proper function.
Lymphatic System and Cancer: Unraveling the Link in Feline Health
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of felines. However, when it comes to the link between the lymphatic system and cancer in cats, there is still much to be understood. Cancer occurs when abnormal cells divide and proliferate uncontrollably, forming tumors that can potentially spread throughout the body. In some cases, these cancerous cells can infiltrate the lymphatic system, causing disruption and complications in feline health. Researchers are actively working to unravel the connection between the lymphatic system and cancer in cats, with the aim of improving diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of this devastating disease.
Understanding how cancer affects the lymphatic system is crucial in identifying potential biomarkers and developing targeted therapies. It is believed that certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma, can directly originate within the lymphatic system itself. Additionally, cancer cells from other parts of the body have the ability to metastasize, or spread, to the lymph nodes through the lymphatic vessels. This can lead to the enlargement of lymph nodes, known as lymphadenopathy, which is often one of the first signs of cancer in cats. By studying the mechanisms involved in lymphatic spread of cancer, researchers hope to discover new ways to intervene and halt the progression of the disease, ultimately improving the prognosis for feline patients.
What is the lymphatic system in feline health?
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that play a crucial role in feline immunity and overall health.
What is the function of lymph nodes in the feline lymphatic system?
Lymph nodes serve as important filtering stations, where immune cells monitor and purify the lymphatic fluid before it returns to the bloodstream.
How do lymphatic vessels contribute to feline immunity?
Lymphatic vessels transport lymph, a clear fluid containing immune cells, throughout the body, helping to defend against infections and diseases.
What are primary lymphoid organs in feline health?
Primary lymphoid organs, such as the bone marrow and thymus, are where feline lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, are produced and matured.
What are secondary lymphoid organs and their role in feline immunity?
Secondary lymphoid organs, including the spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils, act as meeting points for immune cells, facilitating their interaction and response to pathogens.
How does lymphatic drainage work in feline health?
Lymphatic drainage is the process by which excess fluid, waste products, and pathogens are collected and transported by lymphatic vessels to the lymph nodes for further processing and filtration.
How do feline lymph nodes purify the lymphatic system?
Lymph nodes contain specialized immune cells that filter and remove foreign substances, toxins, and pathogens from the lymph, helping to maintain a healthy lymphatic system.
How does the lymphatic system impact feline health in the case of infections?
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in combating infections in felines by transporting immune cells to the site of infection, facilitating the immune response, and helping to eliminate infectious agents.
What is the link between the lymphatic system and cancer in feline health?
Researchers are studying the connection between the lymphatic system and cancer in cats, as abnormalities in lymphatic function can contribute to the development, spread, and treatment of feline cancers.